comparing a designated representative of each category. The chosen primates for this assignment are as
follows (with their grouping in parentheses):
- Lemurs (Prosimians/Strepsirhini)
- Spider Monkey (New World Monkey/Platyrrhini)
- Baboon (Old World Monkey/Cercopithecidae)
- Gibbon (Lesser ape/Hylobatidae)
- Chimpanzee (Great ape/Hominidae)
2. The traits you will be comparing across these five primates will be distributed alphabetically across the class.
Only compare this one assigned trait! Check the list below and locate the trait you will be analyzing for your
blog post by finding the topic next to the letter grouping that matches the first letter in your last name:
- IJKLM: Dentition patterns
3. For each of the five primates you will provide three sets of information:
Lemurs
Lemurs
- a. A thorough description of the environment in which the primates lives.
- They are native to the Madagascar. Most Lemurs are arboreal, living in trees; they spend most of their time at the top of the rain forest canopy or in the forest mid level.
- b. A description of your specified character trait for that primate.
- Their dentition is heterodent, which is having multiple tooth morphologies. Their dental formula is
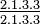 . Their dentition pattern is 2 incisors, 1 canine, 3 premolars, and 3 premolars.
. Their dentition pattern is 2 incisors, 1 canine, 3 premolars, and 3 premolars. - c. A discussion on how the primate’s trait expression has been influenced by its environment, i.e., how can the trait be viewed as an adaptation to the primate’s environment.
- Prosimians have a tooth-comb; which is six of their teeth that are closely pushed together. Leaf eating Lemurs have a little tooth-comb. The fruit eating Lemurs use their tooth-comb to pick out seeds from the fruit.
Spider Monkeys
- a. A thorough description of the environment in which the primates lives
- Spider Monkeys are form the South America and Central America; like Lemurs, Spider Monkeys are also arboreal. They spend most of their time in the upper canopy of the rain forest.
- b. A description of your specified character trait for that primate.
- The Spider Monkeys dental formula is
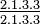 . Their dentition pattern is 2 incisors, 1 canine, 3 premolars, and 3 premolars.
. Their dentition pattern is 2 incisors, 1 canine, 3 premolars, and 3 premolars. - c. A discussion on how the primate’s trait expression has been influenced by its environment, i.e., how can the trait be viewed as an adaptation to the primate’s environment.
- Spider Monkeys are fruit eaters; they use their incisors to pick fruits off of the trees.
- a. A thorough description of the environment in which the primates lives
- Baboons are found in Ethiopia, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen.The have shown us that they can survive almost everywhere, such as the savanna and other semi-arid habitats, and tropical forests.
- b. A description of your specified character trait for that primate.
- Baboons dental formula is
 . They have 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, and 3 molars.
. They have 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, and 3 molars. - c. A discussion on how the primate’s trait expression has been influenced by its environment, i.e., how can the trait be viewed as an adaptation to the primate’s environment.
- Baboons eat grass, leaves, and sometimes eat fish, and other small animal. The trait can be viewed as an adaption because it allows the dentition to be omnivorous.
Gibbons
- a. A thorough description of the environment in which the primates live.
- Gibbons are found in southeast Asia, and parts of southern China. They live in a tropical and subtropical rain forests.
- b. A description of your specified character trait for that primate.
- Their dental formula is
 ; they have 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, and 3 molars.
; they have 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, and 3 molars. - c. A discussion on how the primate’s trait expression has been influenced by its environment, i.e., how can the trait be viewed as an adaptation to the primate’s environment.
- Gibbons, mostly eat fruit, which is every where in their environment. You can believe that their teeth have adapted to their environment in order to eat their food.
Chimpanzee
- a. A thorough description of the environment in which the primates lives.
- Chimpanzee's can be found in Africa; they live in rain forests and savanna's
- b. A description of your specified character trait for that primate.
- Their dental formula is the same as Gibbons, and Baboons, which is
 . They have 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, and 3 molars.
. They have 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, and 3 molars. - c. A discussion on how the primate’s trait expression has been influenced by its environment, i.e., how can the trait be viewed as an adaptation to the primate’s environment.
- The Chimpanzee's diet is a very wide variety of food, which is from plants and small animals. This means that their teeth has adapted to the need of eating basically everything.
4. Summarize your findings, evaluating the level of influence the environment has on the expression of physical
and behavioral traits.
- Studying these primates dentition patterns, we can conclude that the environment and the type of food make an impact on the primates dental structure. As you can see, Spider Monkeys and Lemurs have the same dental formula 2133, which means they are new world monkeys. They live in a similar environment and eat similar foods. The last three, which are, Baboons, Gibbons, and Chimpanzee have the same dental formula (2123); this makes them old world monkeys. The three primates share a similar environment and food. This makes the environment and the food type important to the dental structure.

.jpg)







I don't know why some of my sentences are highlighted with white. Is there a way i can fix it.
ReplyDeleteIf you added the dental formulas copying it from another program, it will bring its formatting with it. Don't worry about. Not a big deal.
ReplyDeleteFirst of all, thank you for the great dental images. They are wonderful.
When I look at your dental descriptions, the only real difference I see is the number of premolars (3 or 2). So when you say that the teeth are adaptations to the diet, is it only in their number of premolars? Baboons, gibbons and chimps share the same dental formula. So why do they have different diets? Or are their other dental differences to talk about? Size of teeth, flatness of molars, cusp height, jaw shape? More description of differences was needed to justify your conclusion that environmental differences lead to dental differences.